-Dr. Buddhi Malla
Leadership, the art of guiding and motivating individuals toward common goals, encapsulates an accumulation of qualities and styles. The essence of exemplary leadership, emphasizing traits such as effective communication, decisive decision-making, and adept interpersonal skills. Indeed, great leaders inspire trust, foster collaboration, and empower their teams to reach their fullest potential. Essential to this is the ability to set clear visions, offer guidance, and lead by example, all while exhibiting adaptability, empathy, and the courage to make tough decisions for the collective good. Successful leaders value feedback, encourage innovation, and cultivate positive organizational cultures, recognizing that leadership is ultimately about driving positive change and achieving success through the collective efforts of a motivated team.
Within the realm of leadership lie various styles, each with its distinct characteristics and implications. Let us delve into a comprehensive examination of these leadership styles and their characteristics.
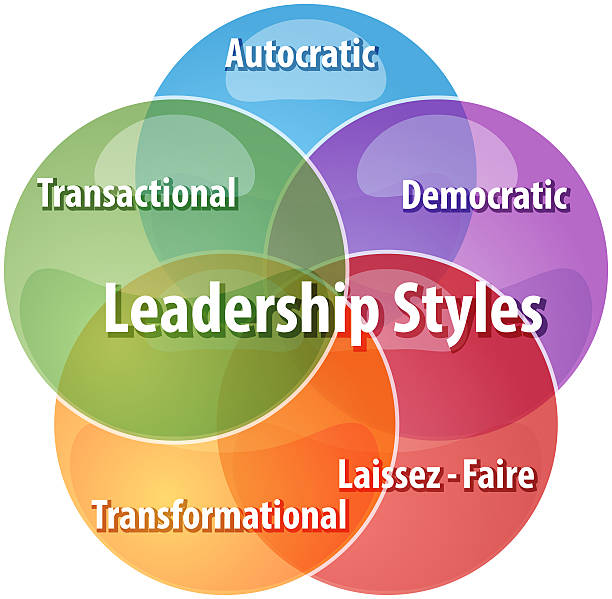
- Autocratic Leader: Autocratic leaders dictate decisions without seeking input from their team, maintaining complete control and enforcing strict hierarchies. While this approach may expedite decision-making, it often stifles creativity and motivation, leading to disempowerment among team members.
- Democratic Leader: These types of leaders engage team members in decision-making, valuing their input and fostering collaboration and open communication. This style nurtures empowerment and accountability, resulting in heightened motivation, creativity, and engagement.
- Transformational Leader: Transformational leaders inspire and motivate by fostering innovation, creativity, and a shared vision. They empower followers to surpass expectations through charisma and passion, driving positive change and leaving a lasting impact.
- Transactional Leader: These verities of leaders maintain the status quo through structured systems of rewards and punishments, emphasizing clear guidelines and performance expectations. While effective in managing tasks and maintaining stability, this style may lack in fostering intrinsic motivation and creativity.
- Servant Leader: Servant leaders prioritize the well-being and development of their followers, exhibiting humility, empathy, and a commitment to nurturing individual growth. By fostering collaboration and empowerment, they inspire trust and strive to meet the needs of those they lead.
- Charismatic Leader: This class of leaders captivates and inspires through charm and vision, rallying others around a shared mission. Their infectious energy and persuasive communication instill belief and enthusiasm, driving the passionate pursuit of collective goals.
- Laissez-Faire Leader: Laissez-faire leaders adopt a hands-off approach, granting autonomy and decision-making authority to team members. While promoting creativity and self-direction, this style may lead to ambiguity and a lack of accountability if not effectively managed.
- Bureaucratic Leader: These kinds of leaders adhere strictly to rules, procedures, and hierarchy, prioritizing stability and predictability. While emphasizing precision and consistency, this approach may hinder agility and innovation if not balanced with flexibility.
- Strategic Leader: Strategic leaders possess a forward-thinking mindset, envisioning and executing long-term plans aligned with organizational goals. By fostering innovation and adaptability, they navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
- Visionary Leader: This category of leaders inspires others with a compelling future, motivating teams to pursue ambitious goals. By instilling purpose and direction, they drive innovation and guide organizations toward meaningful achievements.
- Coach-style Leader: Coach-style leaders prioritize the development and growth of team members, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and success through effective communication and personalized guidance.
- Pacesetting Leader: This sort of leader sets high-performance standards, leading by example. While motivating, this style may lead to excessive pressure and hinder long-term development without adequate support.
- Situational Leader: Situational leaders adapt their style to suit specific contexts and team needs, providing tailored guidance and support for optimal effectiveness.
- Authoritarian Leader: Such a type of leader asserts strong control over decision-making, prioritizing efficiency but risking stifling creativity and motivation.
- Collaborative Leader: Collaborative leaders prioritize teamwork, open communication, and shared decision-making, fostering innovation, trust, and collective success.
- Adaptive Leader: leaders who are adaptive, navigate change with flexibility and resilience, effectively steering organizations through challenges and capitalizing on opportunities.
- Inspirational Leader: Inspirational leaders motivate and energize teams through a compelling vision and passion for their work, fostering commitment and driving meaningful change.
- Ethical Leader: These leaders prioritize integrity, fairness, and transparency, serving as role models for ethical conduct and cultivating a culture of respect and responsibility.
- Innovative Leader: Innovative leaders constantly seek creative solutions to challenges, fostering a culture of experimentation and driving progress and innovation.
Good leaders exemplify qualities like empathy, integrity, and vision, inspiring trust, effective communication, and fostering collaboration. They prioritize their team’s well-being, setting an empowering example for others to follow. Bad leaders lack transparency, accountability, and humility, potentially creating a toxic work environment through manipulation and self-serving actions and Ugly leaders display traits of arrogance, aggression, and incompetence, alienating their team and undermining morale through chaotic, inconsistent leadership without clear direction.
In summary, leadership styles encompass both Theory X and Theory Y of motivation, where Theory X stands for autocratic principles and Theory Y stands for democratic principles. Organizations must recognize the importance of empowering their teams, nurturing creativity, and cultivating positive work environments for sustained success. Leaders must transcend the demotivating aspects of Theory X (Autocratic principles of motivation) and embrace the ethos of Theory Y (Democratic principles of motivation), fostering a culture of engagement, innovation, and growth. Proficient leaders adept at adapting their styles to the ever-evolving landscape are essential in driving positive change and achieving collective success.
-Author Dr. Buddhi Malla is a Banker.